The Corticospinal System Exerts __________
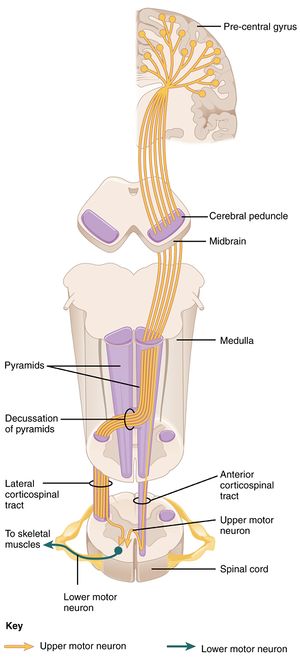
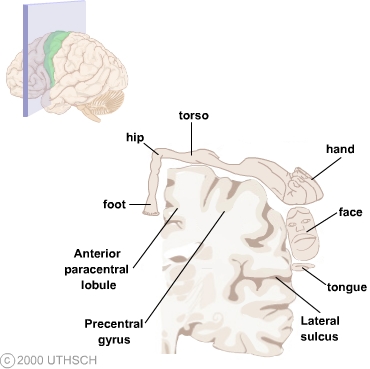
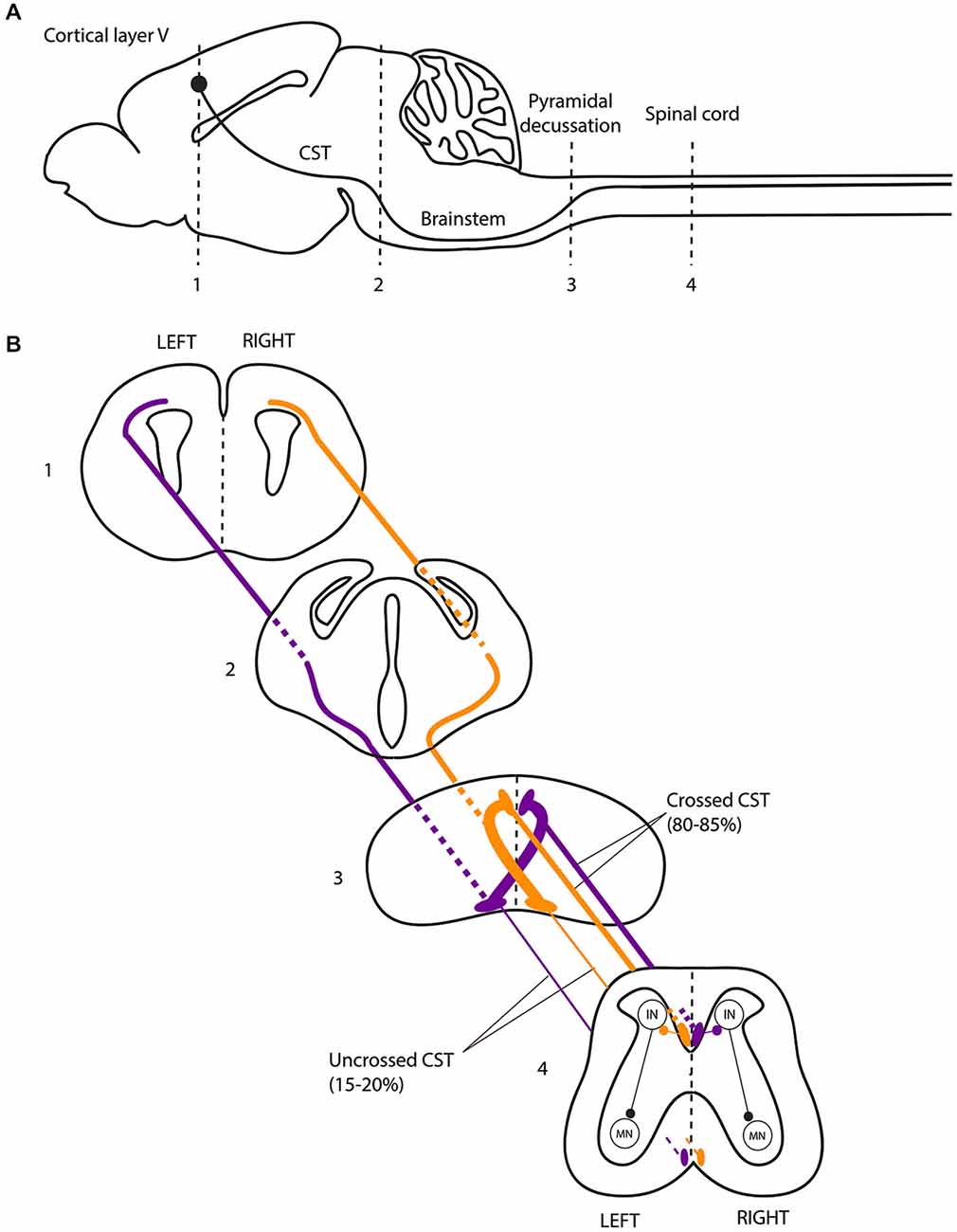
The corticospinal system exerts __________. Vestibulospinal projections were also present early in evolution for control of equilibrium and postural activities. 202 The area of the motor cortex that is devoted to a particular region of the body is proportional to the. The corticospinal tract also known as the pyramidal tract is one of the descending spinal tracts necessary for the passing of information from the central nervous system to the peripheral nervous system particularly to musculature of the axial region of the body the trunk and distal regions limbs and fingerstoes.
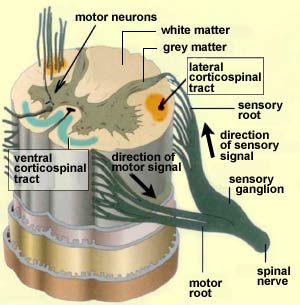
201 The corticospinal system often referred to as the A red. The corticospinal tract or pyramidal tract is a descending white matter tract primarily concerned with motor function extending from the motor cortex down to synapse with motor neurons of the spinal cord in the anterior horns. This highlights the need for proprioceptive monitoring of movements to ensure their accurate execution.
The path starts in the motor cortex where the bodies of the first-order neurons lie. Hence corticospinal drives must be sculpted continuously to compensate for the changing functional efficacy of the descending systems which activate the motoneurones. Corticospinal fibers are axons from upper motor neurons in the cerebral cortex.
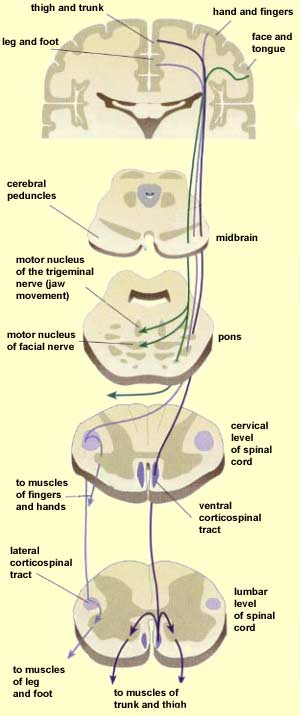
The corticospinal tract is a motor pathway that carries efferent information from the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord. Full article at Acta Physiol 2010 98 4 403-16. Although it is well known that the corticospinal system exerts more influence over distal hand and fingers than proximal elbow and shoulder upper limb muscles differences in the importance of this system for voluntary activation of these muscle groups have not been demonstrated directly.
Two investigations were carried out to provide a quantitative. The direct pathway is via the pyramidal system which includes the corticospinal pyramidal tract together with fibers that diverge from it to innervate cranial nerve motoneuronsthe corticobulbar tract Fig. This baseline respiratory activity of the SMA probably represents an equipoise from which it is easy to move in either direction facilitation or inhibition.
The corticospinal tract is a white matter motor pathway starting at the cerebral cortex that terminates on lower motor neurons and interneurons in the spinal cord controlling movements of the limbs and trunk. This review explores to what extent descending pathways are highly conserved across species and concludes that there are actually rather widespread species differences for example in the transmission of information from the corticospinal tract to upper limb motoneurons. Each of the descending pathways involved in motor control has a number of anatomical molecular.
Novel evidence that intrinsic activity in the human motor cortex modulates input gain along the beta oscillatory cycle within distinct circuits is provided which may lead to new brain state-dependent and circuit-specific interventions for targeted neuromodulation. 248 to 2410 Figs.
This study determined whether the aberrant pattern of CS tract terminations and motor impairments produced by early postnatal M1 activity restriction could be abrogated by reducing activity-dependent synaptic competition from the initially active M1 later in development and reorganization of CS terminals reveals an unsuspected late plasticity after the critical period.
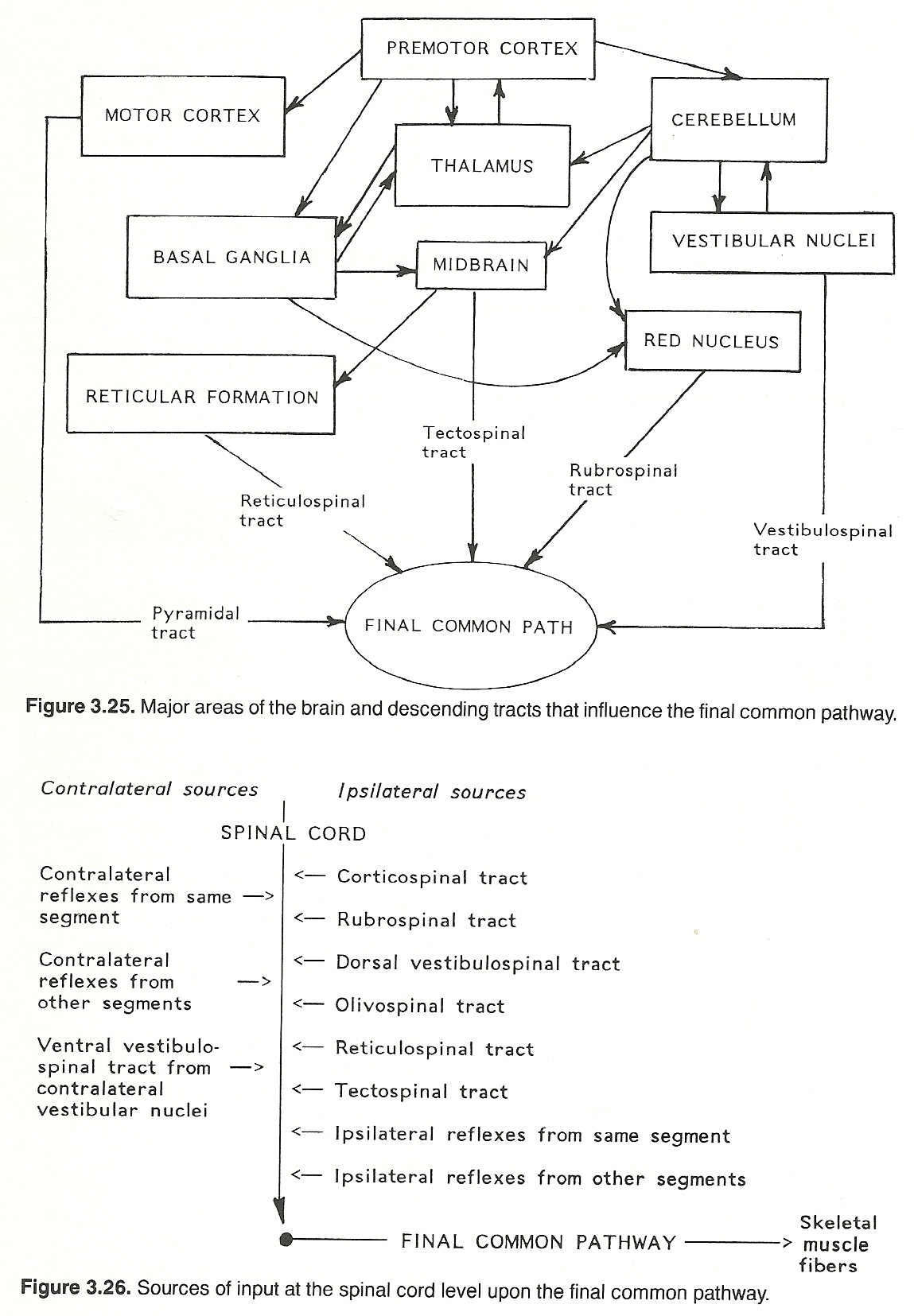
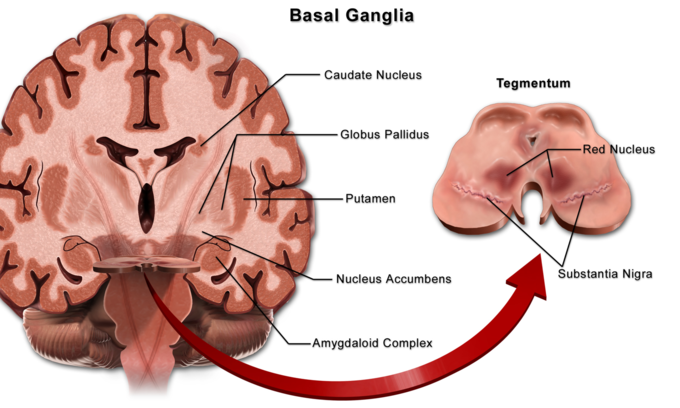
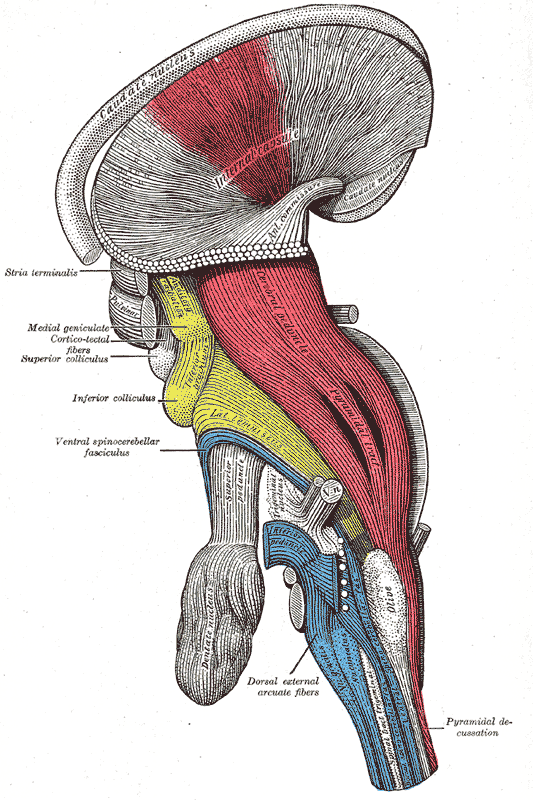
The corticospinal tract also known as the pyramidal tract is one of the descending spinal tracts necessary for the passing of information from the central nervous system to the peripheral nervous system particularly to musculature of the axial region of the body the trunk and distal regions limbs and fingerstoes. Gross anatomy Central connections. There are more than one million neurons in the corticospinal tract and they become myelinated usually in the first two years of life. 201 The corticospinal system is often referred to as the. Although it is well known that the corticospinal system exerts more influence over distal hand and fingers than proximal elbow and shoulder upper limb muscles differences in the importance of this system for voluntary activation of these muscle groups have not been demonstrated directly. Two investigations were carried out to provide a quantitative. Because reticulospinal systems primarily influence extensor muscles including the paravertebral extensors as well as those of the limbs the corticoreticulospinal system may provide the cortex with the means to influence extensor musculature in parallel with its regulation of flexors see Figs. Exerts control over ans system as well as regulating pituitary function. This baseline respiratory activity of the SMA probably represents an equipoise from which it is easy to move in either direction facilitation or inhibition.
Although it is well known that the corticospinal system exerts more influence over distal hand and fingers than proximal elbow and shoulder upper limb muscles differences in the importance of this system for voluntary activation of these muscle groups have not been demonstrated directly. There are more than one million neurons in the corticospinal tract and they become myelinated usually in the first two years of life. Abstract Rhythmic synchronization of neurons is known to affect neuronal interactions. The cerebrum exerts control of voluntary somatic motor activity through several descending pathways. The corticospinal tract is a white matter motor pathway starting at the cerebral cortex that terminates on lower motor neurons and interneurons in the spinal cord controlling movements of the limbs and trunk. Gross anatomy Central connections. Although it is well known that the corticospinal system exerts more influence over distal hand and fingers than proximal elbow and shoulder upper limb muscles differences in the importance of this system for voluntary activation of these muscle groups have not been demonstrated directly.
















:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/anterior-corticospinal-tract/U5jHyC665D7g8ExhRLJN6w_Anterior_corticospinal_tract.png)


















Posting Komentar untuk "The Corticospinal System Exerts __________"