Invasive Pneumococcal Disease Definition
Invasive pneumococcal disease definition. Invasive pneumococcal disease IPD is a notable cause of morbidity and mortality in the US despite the. One Member State used the EU-2002 case definition and four Member. Pneumococcal infections can range from ear and sinus infections to pneumonia and bloodstream infections.
Due to these diagnostic problems epidemiological studies generally define invasive pneumococcal disease IPD as isolation of S. Isolation of Streptococcus pneumoniae from a normally sterile site by culture OR 2. Pneumoniae isolated from a normally sterile site eg CSF blood joint fluid pleural fluid pericardial fluid etc.
Invasive pneumococcal disease Case Definitions Invasive Pneumococcal Disease IPD Streptococcus pneumoniae 2017 Case Definition httpswwwncdcgovnndssconditionsinvasive-pneumococcal-diseasecase-definition2017. These include a middle ear infection a blood infection pneumonia or bacterial meningitis. There are vaccines to help prevent pneumococcal disease.
It can also cause more serious infections of the blood or brain. Invasive Pneumococcal Disease IPD is defined as Streptococcus pneumoniae S. The major clinical syndromes of invasive pneumococcal disease include pneumonia bacteremia and meningitis.
Pneumococcal disease invasive case definition 1. The National Advisory Committee on Immunization NACI recommends immunization against pneumococcal disease. For Health Professionals Invasive pneumococcal disease IPD is an acute and serious communicable disease caused by the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Pneumoniae from blood or another normally sterile site. Pneumococcal noo-muh-KOK-uhl disease is a name for any infection caused by bacteria called Streptococcus pneumoniae or pneumococcus. 2 Normally sterile sites include.
1 Clinical illness associated with invasive disease manifests itself mainly as pneumonia with bacteremia bacteremia without a known site of infection and meningitis. The bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae S.
Pneumoniae from normally sterile sites.
Invasive Pneumococcal Disease IPD is defined as Streptococcus pneumoniae S. Pneumonia without bacteremia is not reportable. Invasive Pneumococcal Disease IPD is defined as Streptococcus pneumoniae S. Laboratory Criteria For Diagnosis. In 2016 29 Member States reported data on invasive pneumococcal disease IPD. Invasive disease means that germs invade parts of the body that are normally free from germs. These include a middle ear infection a blood infection pneumonia or bacterial meningitis. Invasive disease may lead to several syndromes including meningitis and bacteremia. Pneumoniae by culture andor detection of nucleic acid of S.
Twenty-four Member States used the EU-20082012 case definition. Invasive disease may lead to several syndromes including meningitis and bacteremia. For Health Professionals Invasive pneumococcal disease IPD is an acute and serious communicable disease caused by the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae. Pneumoniae isolated from a normally sterile site eg CSF blood joint fluid pleural fluid pericardial fluid etc. It can also cause more serious infections of the blood or brain. The major clinical syndromes of invasive pneumococcal disease include pneumonia bacteremia and meningitis. Due to these diagnostic problems epidemiological studies generally define invasive pneumococcal disease IPD as isolation of S.




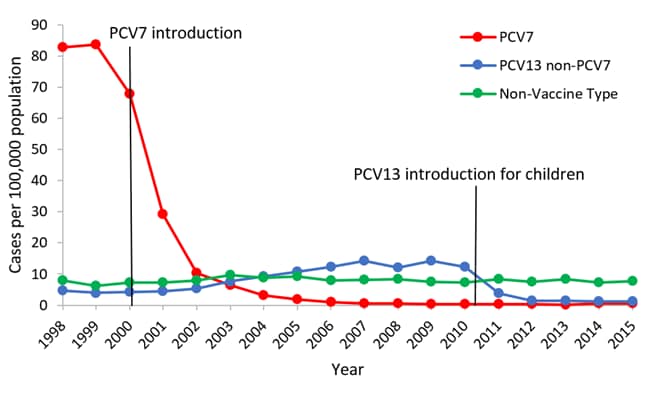










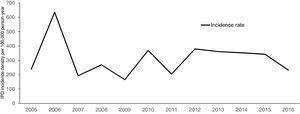
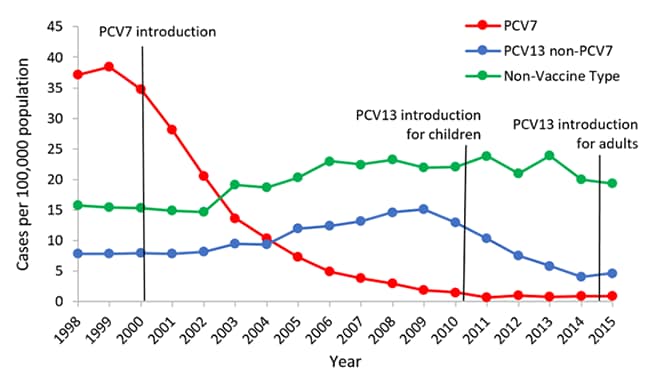
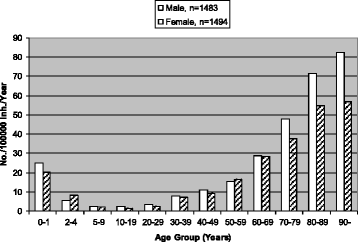
























Posting Komentar untuk "Invasive Pneumococcal Disease Definition"