Obstructive Lung Disease Flow Volume Loop
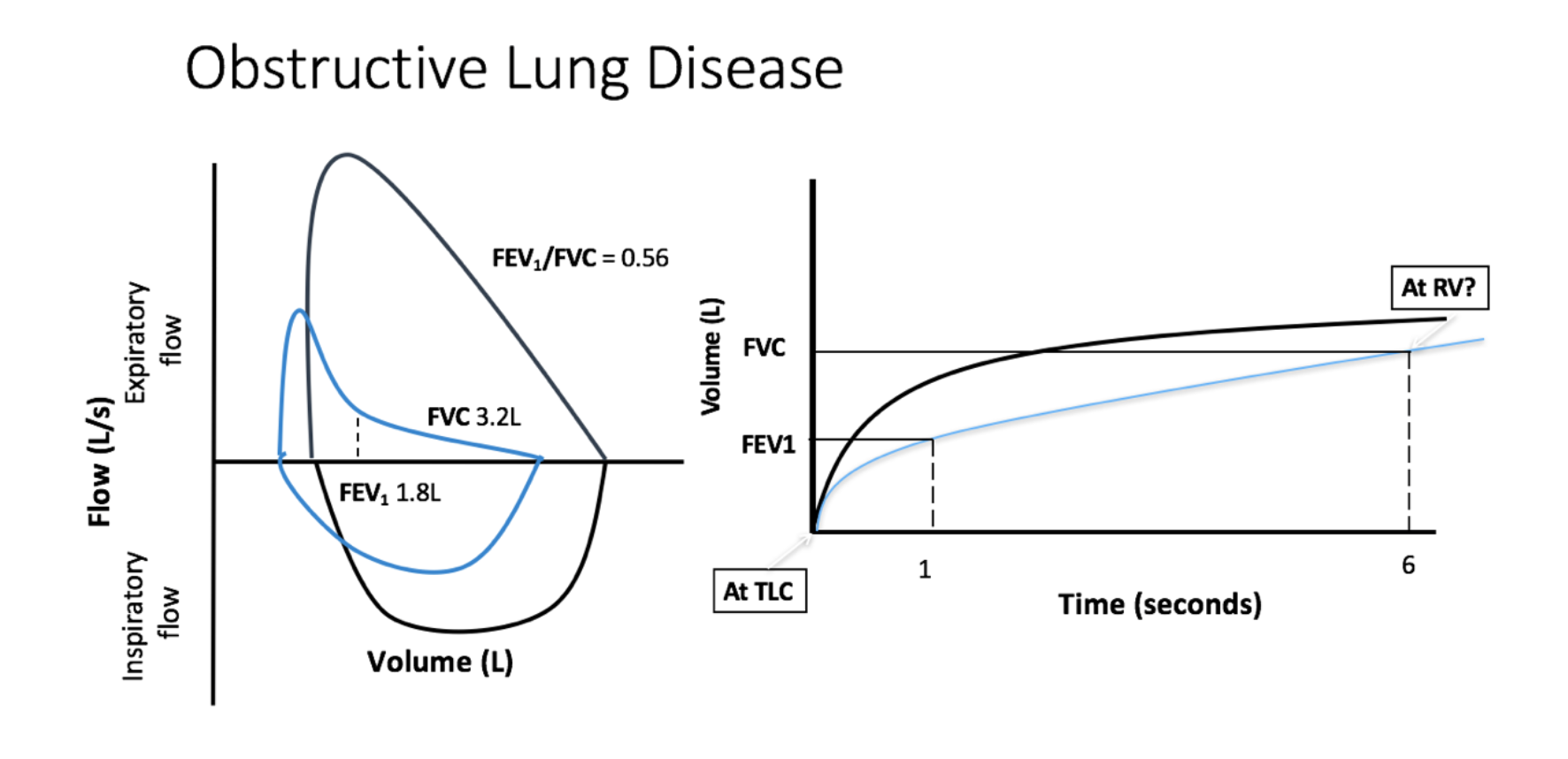
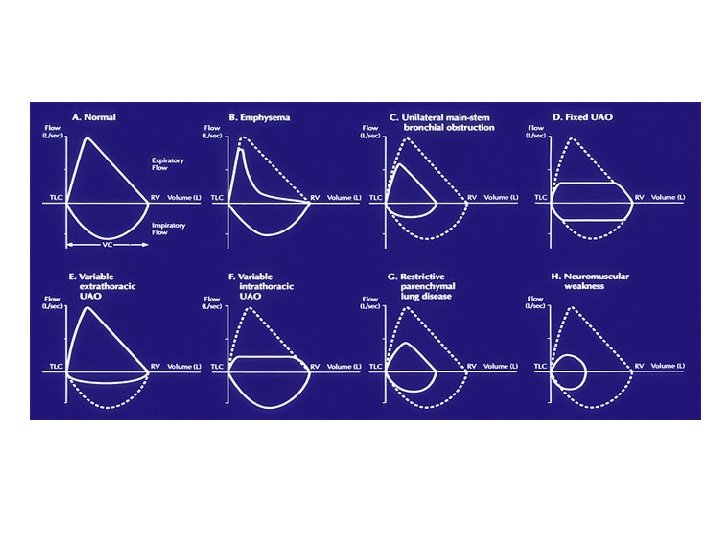
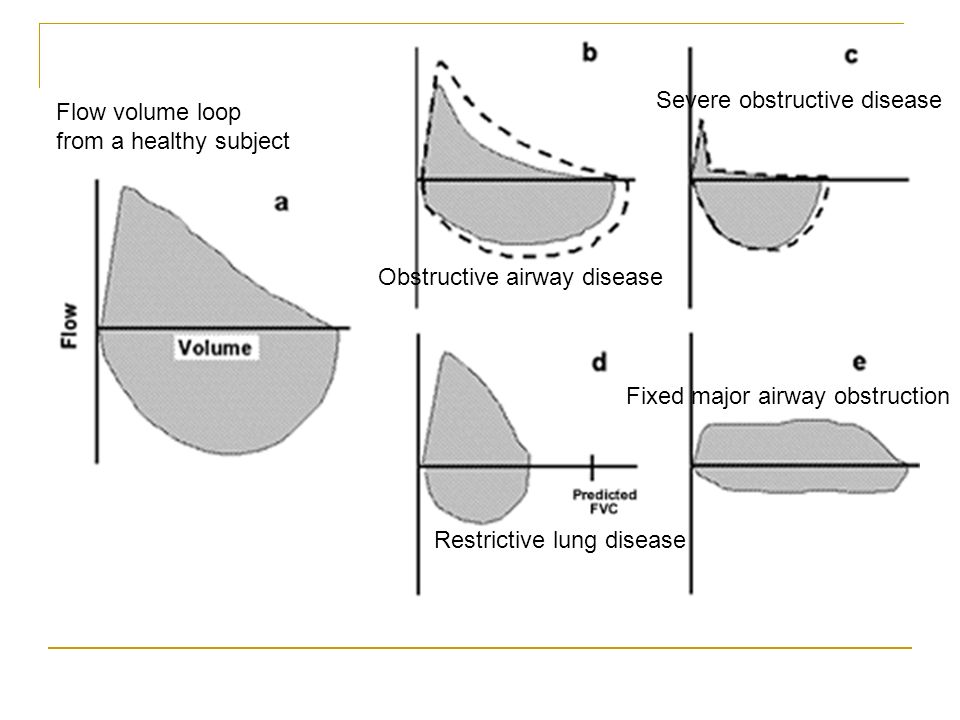
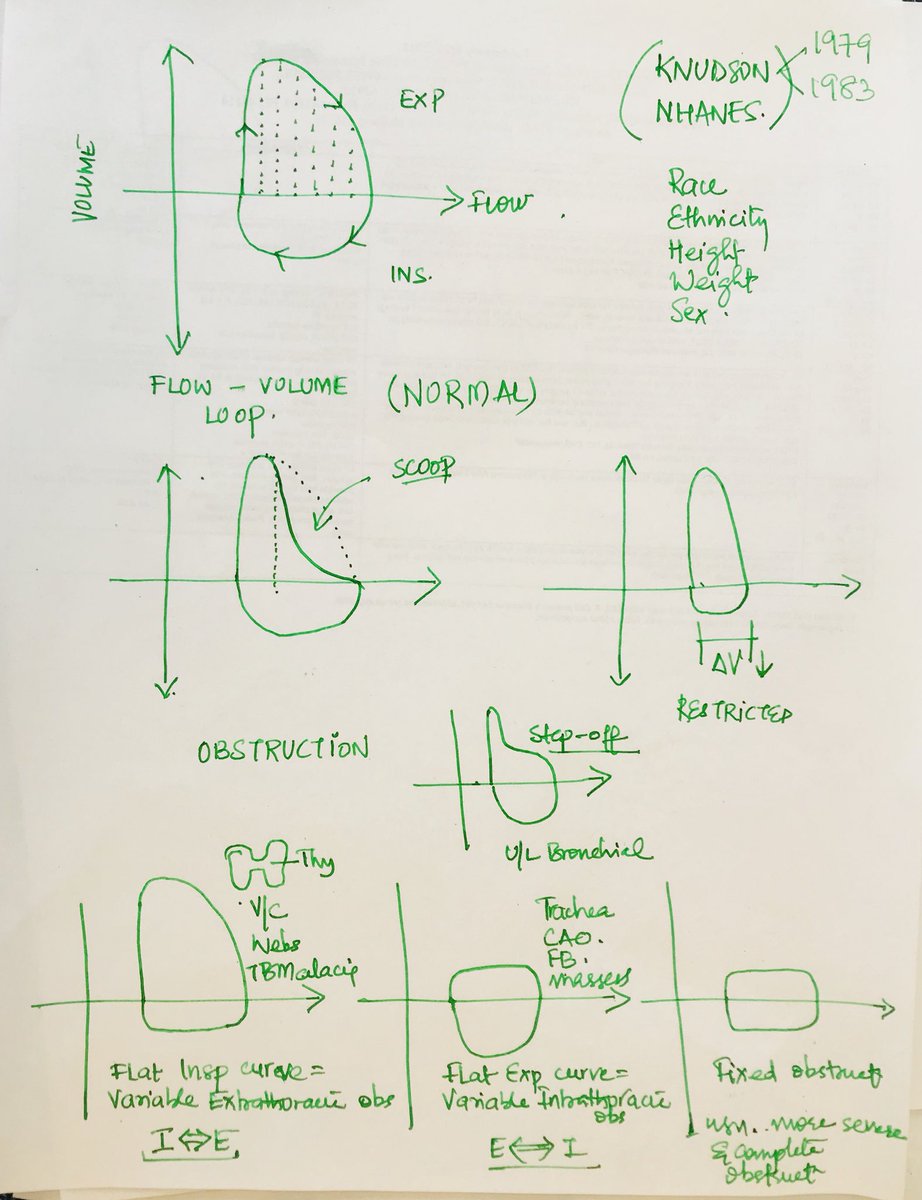
Obstructive lung disease flow volume loop. In common obstructive airflow disorders eg. The location of the airway obstruction can also be identified from the shape of the flow volume loop. When obstructive lung disease is present often a post-medication test is performed after administration of a bronchodilator like ventolin.
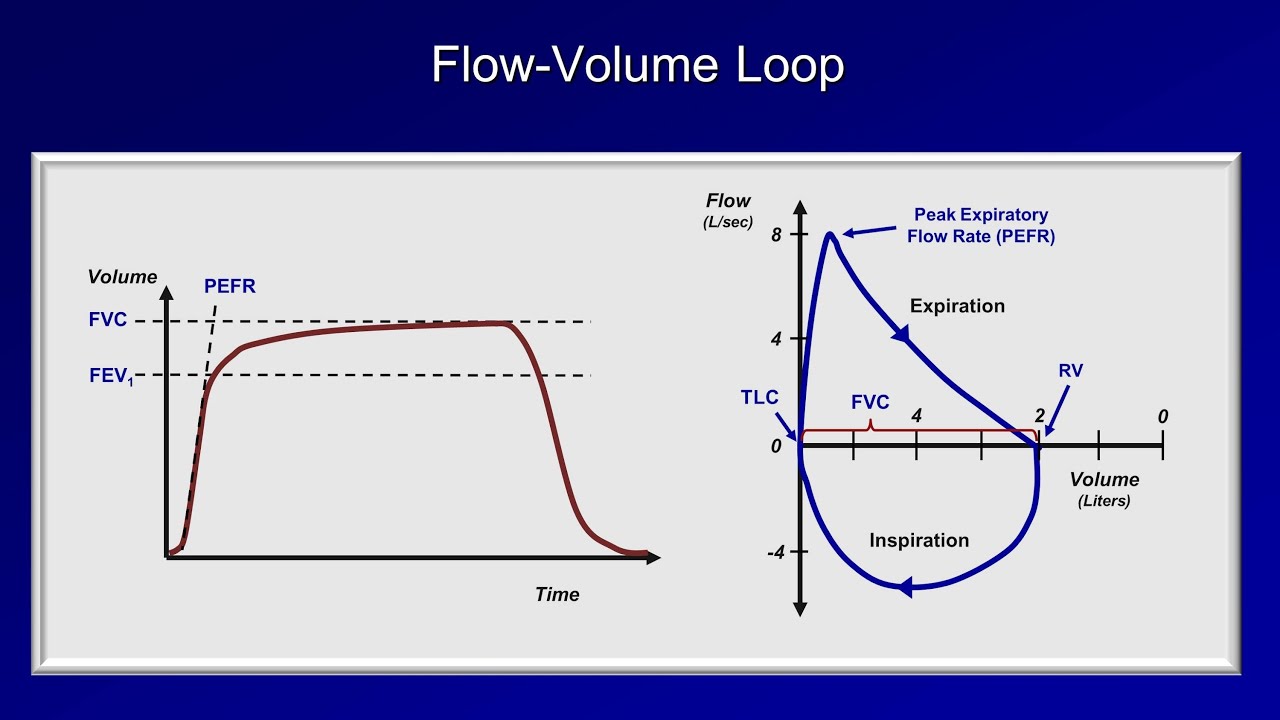
Along with spirometry a flow-volume loop is also typically generated. Measurements are typically reported as absolute flows and volumes and as percentages of predicted values using data derived from large populations of people presumed to. Analyzing flow volume loops provides a quick way to detect lung disease.
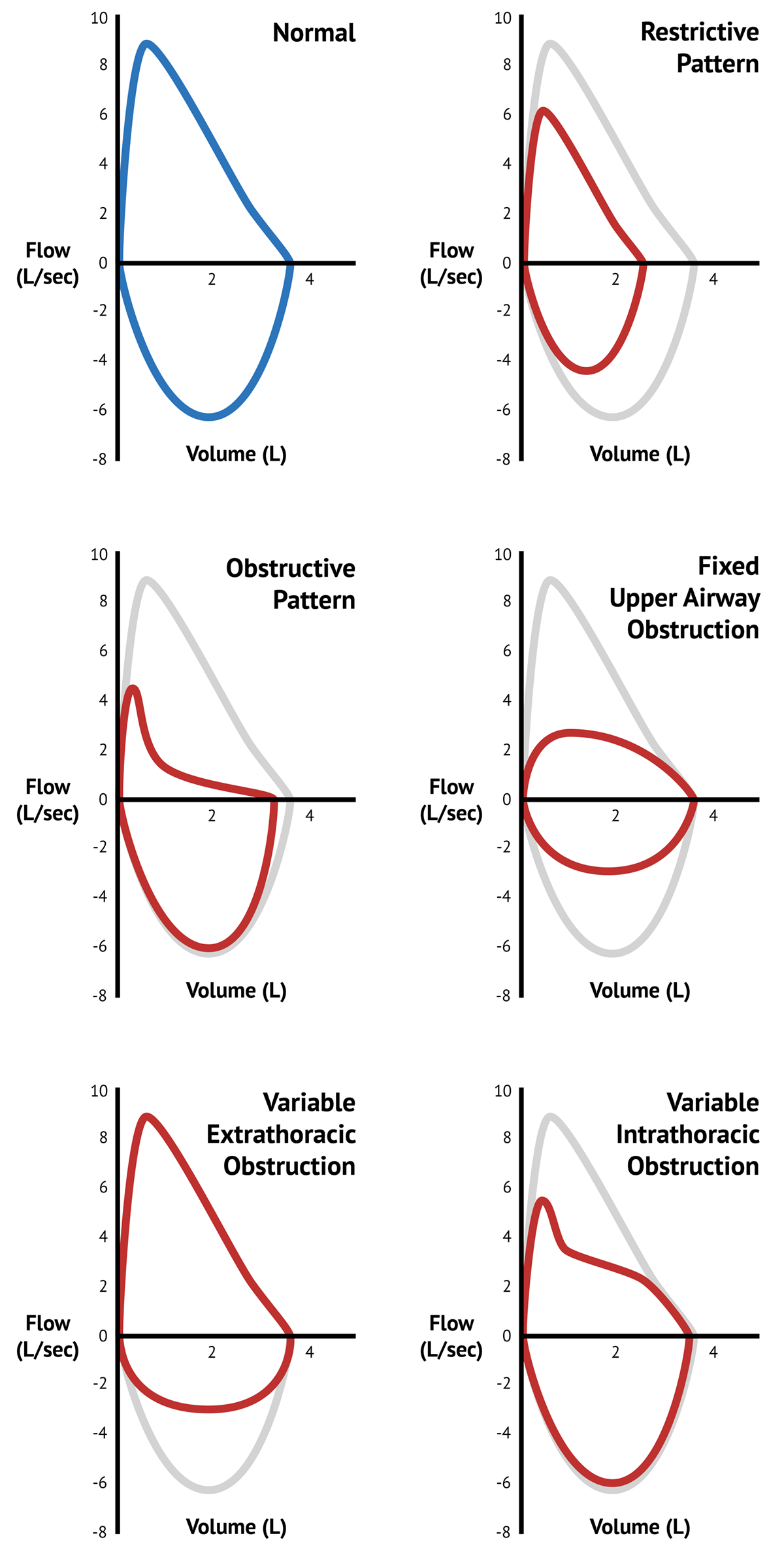
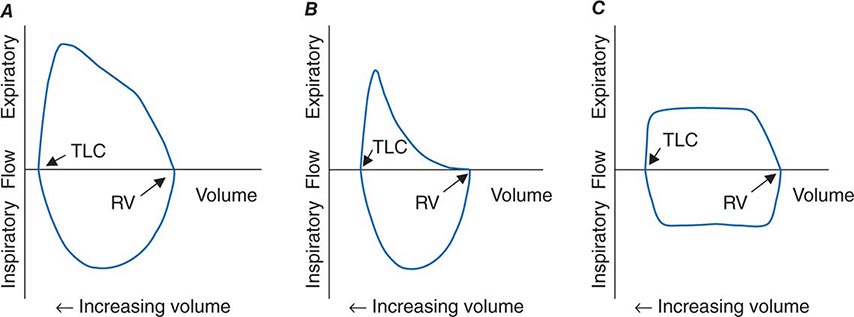
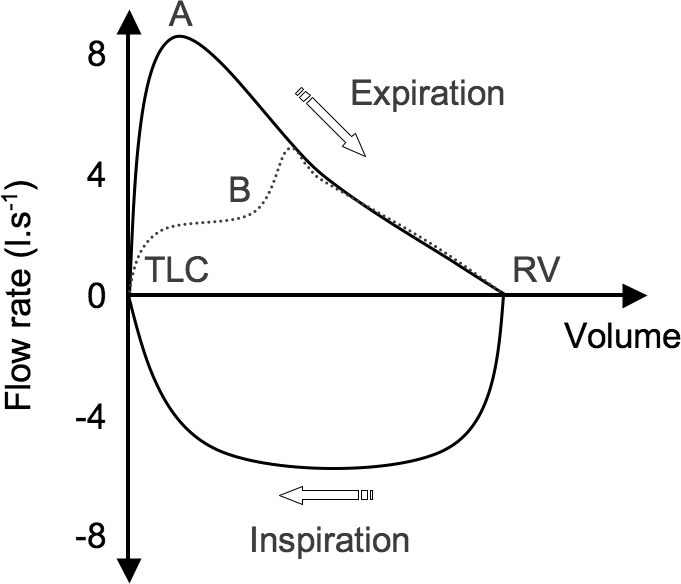
Occurs at beginning of forced expiration. A normal flow volume loop Figure 1a has a characteristic shape. The shape of the flow-volume loop can indicate the location of airflow limitation such as the.
Spirometry flow-volume measurement is used routinely in the outpatient setting to rule out obstructive lung diseases. Low peak inspiratory flow Low peak expiratory flow Failure of the expiratory flow curve to reach zero an open loop A scooped out expiratory flow pattern. A flow-volume loop plots flow on the y axis and volume on the x axis.
The curve assumes a. Radial traction distends airways. Normal standards and abnormalities in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
The flow-volume loop obtained during the spirometry manoeuvre can have four distinctive shapes that are linked to certain pathologies. The shape of the flow-volume loop can indicate the location of airflow limitation. Interpret lung volumes Full lung volumes are necessary to assess whether restriction is present Step 3.
Airflow and lung volume measurements can be used to differentiate obstructive from restrictive pulmonary disorders to characterize severity and to measure responses to therapy. Typical flow-volume plots observed with differing.
When obstructive lung disease is present often a post-medication test is performed after administration of a bronchodilator like ventolin.
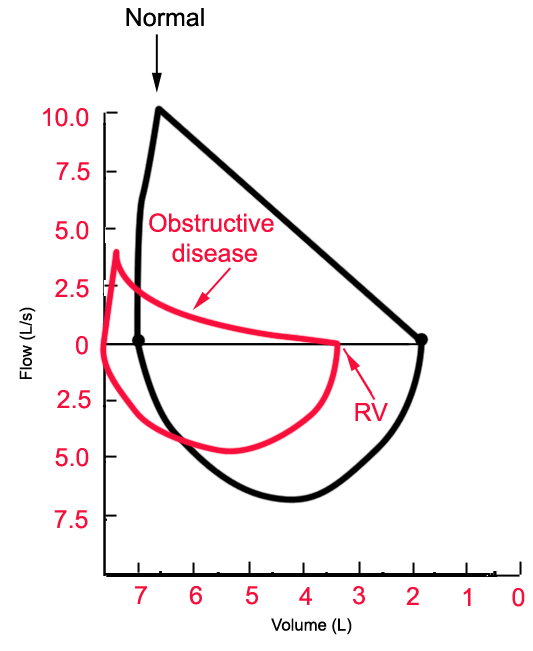
A concave flow-volume loop in a young individual likely indicates the presence of airway obstruction whereas in an elderly individual the same flow-volume loop. The flow-volume loop obtained during the spirometry manoeuvre can have four distinctive shapes that are linked to certain pathologies. Normal Standards and Abnormalities in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease The flow-volume loop is a test of ventilatory function in which a graphic recording of maximal flow rates is displayed at all lung volumes during a maximal effort forced expiratory and inspiratory vital capacity maneuver. Obstructive lung disease is the most common diagnosis of a lung pathology when using a spirometer. A normal flow volume loop Figure 1a has a characteristic shape. The appearance of the loop can reveal the presence of obstructive andor restrictive lung disease. Is there response to bronchodilator. It is usually characterized by some form of airway obstruction. The shape of the flow-volume loop can indicate the location of airflow limitation.
Spirometry flow-volume measurement is used routinely in the outpatient setting to rule out obstructive lung diseases. The Flow Volume Loop. In these patients narrowing obstruction of the smaller bronchi and larger bronchioles occur often because of excessive contraction of the smooth muscle itself. PEF occurred at lower lung volumes in restrictive dise8se nd at higher volumes iD obstructive disease. Measurements are typically reported as absolute flows and volumes and as percentages of predicted values using data derived from large populations of people presumed to. Typical flow-volume plots observed with differing. The flow-volume loop obtained during the spirometry manoeuvre can have four distinctive shapes that are linked to certain pathologies.




































Posting Komentar untuk "Obstructive Lung Disease Flow Volume Loop"